51:1–64 The judgment oracle against Babylon continues, focusing on Babylon’s ultimate destruction. The poetic oracles of judgment are concluded with an account of a symbolic action representing Babylon’s demise in vv. 59–64. |
51:1 Leb-qamai This Hebrew expression means “heart of one who rises against me.” It probably is a coded reference and not a place-name.
51:5 the Holy One of Israel Compare 50:29. This name for God is most frequently used by Isaiah (see note on Isa 1:4).
51:7 a cup of gold in the hand of Yahweh Babylon was Yahweh’s tool to judge the nations. Compare the imagery of the cup of wrath in Jer 25:15–29 and the depiction of Assyria as Yahweh’s tool of judgment in Isa 10:5.
51:11 the kings of the Medes Media was in northwest Iran, the region to the north and east of Babylon. The Medes became a province of Persia in 549 bc and participated in Persia’s takeover of the Babylonian Empire in 539 bc. Compare Isa 13:17; 21:2. See Dan 5:24–30.
was in northwest Iran, the region to the north and east of Babylon. The Medes became a province of Persia in 549 bc and participated in Persia’s takeover of the Babylonian Empire in 539 bc. Compare Isa 13:17; 21:2. See Dan 5:24–30.
51:12 Against the walls of Babylon raise a banner Compare Isa 13:2.
51:14 Yahweh of hosts has sworn by himself See Jer 22:5 and note.
51:15–19 This passage is essentially identical to 10:12–16 and makes use of stock poetic imagery about Yahweh as Creator. See note on 10:12; note on 10:13; note on 10:14; note on 10:16. |
51:15 the one who made the earth by his power Yahweh’s sovereignty over the universe is linked to His creative power.
51:17 All humankind turns out to be stupid, without knowledge See note on 10:14.
51:19 The portion of Jacob See note on 10:16.
51:20 a war club for me, a weapon of battle Compare Isa 10:5 and note.
51:24 wickedness that they have done in Zion Namely, the destruction of the temple. Compare Jer 50:28; 51:11.
51:25 O mountain of the destruction For the image of Babylon as a mountain, see Dan 2:35.
51:27 Ararat, Minni, and Ashkenaz Regions of eastern Turkey, northwest Iran, and the Caucasus—all part of the territory controlled by the Medes (see Jer 51:28).
51:30 they have become as women See Jer 50:37 and note.
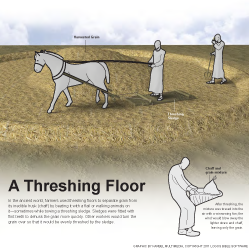
51:33 like a threshing floor A place where grain was beaten off the stalk with a sledge drawn by a pair of oxen. See note on 1 Sam 23:1; note on Isa 28:27.
51:34 Nebuchadnezzar See note on Jer 21:2.
51:41 Sheshach The Hebrew text uses sheshakh for “Babylon” (see 25:26 and note). Sheshach (Sheshak) is an athbash cryptogram. See note on 25:26; note on v. 1.
51:44 Bel Babylon’s chief deity (called both “Bel” and “Marduk”). See note on 50:2.
51:59–64 The lengthy oracle condemning Babylon concludes with a final symbolic action that Jeremiah performs vicariously through the royal official Seraiah, brother of Baruch (see note on 32:12). Seraiah is part of the delegation accompanying King Zedekiah to Babylon in 593 bc. The delegation might have been in response to the rebellion in Syria-Palestine being promoted by Edom, Moab, Tyre, and Sidon (27:3). Perhaps Zedekiah was bringing tribute to Nebuchadnezzar to emphasize his submission and avoid reprisals (see 27:17 and note). Jeremiah gives Seraiah a scroll listing the disasters that will befall Babylon. He commands Seraiah to read the scroll aloud in Babylon, then tie it to a rock and throw it into the Euphrates River. The action symbolizes that the list will come true; the same thing that happened to the scroll will happen to Babylon. |
 Symbolic Actions of the Prophets Table
Symbolic Actions of the Prophets Table
51:59 Seraiah Brother of Baruch. See note on 32:12.
the fourth year of his reign 593 bc. See note on 27:1.
the quartermaster The official responsible for supplies and travel arrangements. His title in Hebrew is literally “chief of resting.”
51:60 one scroll Probably a papyrus scroll. See note on 30:2.
51:63 into the middle of the Euphrates One of the two major rivers of Mesopotamia. See note on 13:4.
51:64 Thus shall Babylon sink Compare the symbolic actions in 19:10–11.

|
About Faithlife Study BibleFaithlife Study Bible (FSB) is your guide to the ancient world of the Old and New Testaments, with study notes and articles that draw from a wide range of academic research. FSB helps you learn how to think about interpretation methods and issues so that you can gain a deeper understanding of the text. |
| Copyright |
Copyright 2012 Logos Bible Software. |
| Support Info | fsb |
 Loading…
Loading…