46:1–51:64 Oracles announcing judgment on foreign nations are common in the Prophetic books. These oracles assert Yahweh’s sovereignty and right to judge the nations. This section of Jeremiah appears to have existed as a separate collection of oracles compiled later, along with other prophetic material from Jeremiah; the ancient Greek translation known as the Septuagint has the entire section in a different location. All the traditional enemies of Israel are mentioned in these oracles. Egypt is mentioned first, following on the judgment announced in 44:1–30. The last two chapters of the section contain lengthy denunciations of Babylon, emphasizing their eventual demise after Yahweh has finished using them as His agents of judgment. |
 Oracles against the Nations Table
Oracles against the Nations Table
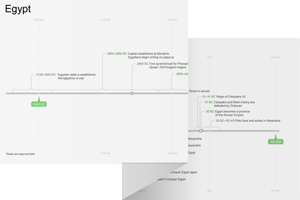
46:1–28 Jeremiah’s oracle of judgment on Egypt focuses on two events: Egypt’s defeat at the battle of Carchemish in 605 bc and Nebuchadnezzar’s later invasion of Egypt around 569–68 bc. |
46:1 concerning the nations This heading introduces the entire collection of oracles against the nations in chs. 46–51 and alludes to Jeremiah’s role as a “prophet to the nations” (1:5).
46:2 Pharaoh Neco Egyptian ruler whose reign corresponded with the reigns of Josiah, Jehoahaz, and Jehoiakim in Judah.
Neco II (or Necho) ruled in Egypt from 609–595 bc. He was part of the Saite (or 26th) Dynasty and the son of Psammetichus I, who founded the dynasty (663–609 bc). Neco was heavily invested in the foreign affairs of Syria-Palestine and Mesopotamia. His military activities in the region had a significant impact on the history of Judah. King Josiah of Judah opposed Neco as Neco was passing through Israelite territory on his way to aid Assyria. Josiah was killed in the ensuing battle at Megiddo in 609 bc (2 Kgs 23:28–30). On his return from Assyria, Neco asserted Egyptian control over Judah by deposing Josiah’s successor, Jehoahaz, and replacing him with another son of Josiah, Jehoiakim (2 Kgs 23:31–35). Jehoiakim was a loyal vassal of Egypt until 604 bc, when Nebuchadnezzar took control of the area after defeating Neco in 605 bc at the Battle of Carchemish. Neco was able to keep Nebuchadnezzar out of Egypt in 601 bc, but Neco’s role in the politics of Syria-Palestine was finished (2 Kgs 24:7). |
Carchemish A city in northern Syria. It was the site of a major battle in 605 bc in which the Babylonians defeated the remnants of the Assyrian army and its Egyptian allies.
Nebuchadnezzar See note on Jer 21:2.
the fourth year of Jehoiakim 605 bc.
46:3 small shield and shield The Hebrew words used here, magen and tsinnah, refer to two sizes of shields.
46:5 Terror is from all around The warriors were preparing for battle in vv. 3–4, but they have been quickly beaten. The Hebrew phrase used here, magor missaviv, appears several times in Jeremiah to describe imminent judgment. See note on 20:3.
46:7 Who is this that rises like the Nile, like the rivers whose waters surge? Jeremiah depicts Egypt’s ambitions of world conquest with the image of rising floodwaters. The annual flood of the Nile was an essential component of Egyptian agriculture.
46:9 Cush and Put Cush (Ethiopia) and Put (Libya) were Egypt’s neighbors to the south and west. See note on Ezek 38:5.
Lud The kingdom of Lud (Lydia) was located in central Turkey. See note on Ezek 27:10.
46:10 to the Lord Yahweh of hosts The ultimate day of judgment against the nations.
a sacrifice is for the Lord Yahweh of hosts Compare Isa 34:6; Zeph 1:7–9.
46:11 to Gilead A region east of the Jordan known for its balm. See Jer 8:22 and note.
there is no healing for you Compare Ezek 30:21.
46:13 the coming of Nebuchadnezzar The Babylonian king attempted to invade Egypt in 601 bc and 568 bc.
46:14 Migdol On Egypt’s northeastern frontier. See note on Ezek 29:10.
Memphis and in Tahpanhes Cities in the Nile delta region. See note on Jer 43:7; note on 44:1; note on Ezek 30:13.
46:17 a roar, he missed the opportunity This statement derides Egypt for bragging but failing to act. The phrase might involve a Hebrew pun on the name of Pharaoh Hophra.
46:18 Tabor among the mountains A prominent mountain on the north side of the Jezreel Valley. Both Tabor and Carmel are important and easily distinguished landmarks.
Carmel by the sea A mountain range on the Mediterranean coast that divided Israel, with the plain of Acco to the north and the plain of Sharon to the south. Modern-day Haifa is on the northwest corner of the Carmel range.
46:19 Pack your baggage for exile Compare Ezek 12:3. Egypt is warned to expect the same fate as Jerusalem.
it will be destroyed, without inhabitant Compare Jer 4:7.
46:20 a gadfly from the north A metaphor for Babylon. Compare Isa 7:18.
46:21 like calves of fattening Ready for slaughter. Compare 1 Sam 28:24.
46:25 Amon of Thebes Amon was an Egyptian sun god whose temple was at Thebes (called “No” in Hebrew). See note on Ezek 30:14.
 Pagan Deities in the Old Testament Table
Pagan Deities in the Old Testament Table
46:26 into the hand of Nebuchadnezzar Compare Ezek 29:19 and note.
it will be inhabited Compare Isa 19:22–25; Ezek 29:13–14.
46:27 my servant Jacob, you must not be afraid A promise of future restoration for Israel and Judah is inserted here to remind Israel that its discipline is temporary. The poetry in Jer 46:27–28 is similar to 30:10–11 and Isa 41:8–10.
46:28 I will not make a complete destruction See Jer 30:11 and note.

|
About Faithlife Study BibleFaithlife Study Bible (FSB) is your guide to the ancient world of the Old and New Testaments, with study notes and articles that draw from a wide range of academic research. FSB helps you learn how to think about interpretation methods and issues so that you can gain a deeper understanding of the text. |
| Copyright |
Copyright 2012 Logos Bible Software. |
| Support Info | fsb |
 Loading…
Loading…

 Pharaoh Neco
Pharaoh Neco 
