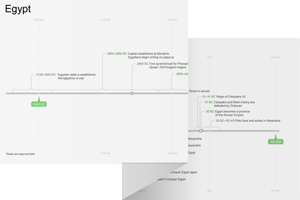
30:1–19 This third oracle against Egypt is the only one without a date. It consists of four segments, each introduced by the Hebrew formula koh amar adonay yhwh (“thus says the Lord Yahweh”). The oracle reuses the imagery of Ezek 29:1–21, pronouncing judgment on Egypt and expanding on the earlier oracle. Ezekiel’s use of “day of Yahweh” imagery echoes 7:10–27. |
30:3 a day is near for Yahweh See note on 7:1–27.
A day of cloud Depictions of clouds or thick darkness is a common part of the Day of Yahweh motif (compare Joel 2:2; Zeph 1:15).
a time of the nations The Hebrew text reads “a time for the nations,” implying the Day of Yahweh is ultimately about judgment against all the nations, not just Egypt.
30:4 a sword will come See Ezek 29:8 and note.
they will take its wealth In 29:19, Yahweh promised the wealth of Egypt to Nebuchadnezzar.
30:5 Cush and Put and Lud Identifies the nations referenced in v. 3. They are major allies and neighbors of Egypt, including: Cush (Nubia or Ethiopia; see note on 29:10); the peoples of the Arabian Peninsula; Lydia in central Asia Minor (see note on 27:10); and two regions of Libya.
30:6 the supporters of Egypt will fall The Egyptian military during the Saite Dynasties (contemporary with Ezekiel) included soldiers from all allies listed in v. 5. Jeremiah 46:9 also lists Cush, Put (Libya), and Lud (Lydia) as part of the pharaoh’s army. Judgment will come on Egypt’s allies because Egypt failed to be a good ally to Judah when needed.
from Migdol to Syene See note on Ezek 29:10. The expression encompasses the entire land of Egypt by referencing a location on either end.
30:9 messengers will go down from before me in the ships An apparent reversal of imagery from Isa 18:1–2, where messengers are dispatched from Cush to Assyria.
30:10 by the hand of Nebuchadnezzar See Ezek 29:19.
30:12 and I will make the Nile streams dry land Alludes to the threats of 29:9–10.
30:13 the worthless idols from Memphis The city of Memphis (called Noph in Hebrew) was one of the ancient capitals of Lower Egypt, located near the beginning of the delta region. Pharaoh Hophra (see note on 29:2) had a palace at Memphis, but it also was an important religious center with temples to many Egyptian gods.
(called Noph in Hebrew) was one of the ancient capitals of Lower Egypt, located near the beginning of the delta region. Pharaoh Hophra (see note on 29:2) had a palace at Memphis, but it also was an important religious center with temples to many Egyptian gods.
there will no longer be a prince Pronounces an end to religious and royal institutions. The pharaoh at this time was Hophra, one of the last kings of the Saite Dynasty in Egypt. After the Saite Dynasty, Egypt was dominated by a succession of foreign empires. The country was annexed by Cambyses of Persia starting in 525 bc, then by Alexander the Great in 332 bc and Rome in 30 bc. Egypt never again enjoyed the status of an autonomous world power.
After the Saite Dynasty, Egypt was dominated by a succession of foreign empires. The country was annexed by Cambyses of Persia starting in 525 bc, then by Alexander the Great in 332 bc and Rome in 30 bc. Egypt never again enjoyed the status of an autonomous world power.
30:14 Pathros The region of Upper Egypt was called Pathros. See note on 29:14.
was called Pathros. See note on 29:14.
Zoan An important city in the northeastern delta region of Egypt. Also known as Tanis, it was the capital city of Egypt during the Israelite monarchy.
in the northeastern delta region of Egypt. Also known as Tanis, it was the capital city of Egypt during the Israelite monarchy.
No Thebes (called No in Hebrew) was the ancient capital city of Upper Egypt and the site of two large temples to the god Amon. It was an important religious center with many other temples and tombs of the kings. Some of the best-preserved monuments in Egypt are in this area, including the temples at Karnak, Luxor, and Medinet Habu.
of Upper Egypt and the site of two large temples to the god Amon. It was an important religious center with many other temples and tombs of the kings. Some of the best-preserved monuments in Egypt are in this area, including the temples at Karnak, Luxor, and Medinet Habu.
30:15 Sin, the stronghold of Egypt Pelusium (called Sin in Hebrew) was the official entry point into Egypt on the northeastern frontier, located on the Mediterranean coast at the far eastern edge of the Delta region.
30:17 On and Pi Beseth These cities are in Lower Egypt in the Nile Delta region. Pi-beseth, also known as Bubastis, is located in the central delta, southwest of Zoan (see note on v. 14). On is also called Heliopolis and is located south of Pi-beseth on the eastern side of the Nile.
30:18 Tahpanhes A village and border outpost in the eastern Nile Delta. Jewish exiles settled there after the fall of Jerusalem in 586 bc, taking the prophet Jeremiah with them against his will (see Jer 43:7).
30:20–26 This oracle can be read as a response to Egypt’s attempted involvement in Judaean affairs in 587 bc. While the Egyptian attack forces the Babylonians to leave Jerusalem, it is not the sign of deliverance that the people of Judah hoped for. Ezekiel warns them against such hopes because Egypt will soon fall. |
30:20 the eleventh year, in the first The date corresponds to April 29, 587 bc, close to the time when Egypt’s invasion of Palestine forced Nebuchadnezzar to temporarily lift the siege of Jerusalem.
30:21 the arm of Pharaoh, the king of Egypt, I have broken The arm symbolizes strength and the ability to wage war. Breaking it symbolizes taking away the power to fight (compare Psa 10:15).
30:23 I will scatter Egypt among the nations See Ezek 29:12 and note.
30:24 I will strengthen the arm of the king of Babylon See note on v. 21.
and I will give my sword into his hand See 29:20. Another explicit indication that Babylon is serving as Yahweh’s agent of judgment. Egypt’s attempted interference in judgment against Judah brought judgment back on itself.

|
About Faithlife Study BibleFaithlife Study Bible (FSB) is your guide to the ancient world of the Old and New Testaments, with study notes and articles that draw from a wide range of academic research. FSB helps you learn how to think about interpretation methods and issues so that you can gain a deeper understanding of the text. |
| Copyright |
Copyright 2012 Logos Bible Software. |
| Support Info | fsb |
 Loading…
Loading…